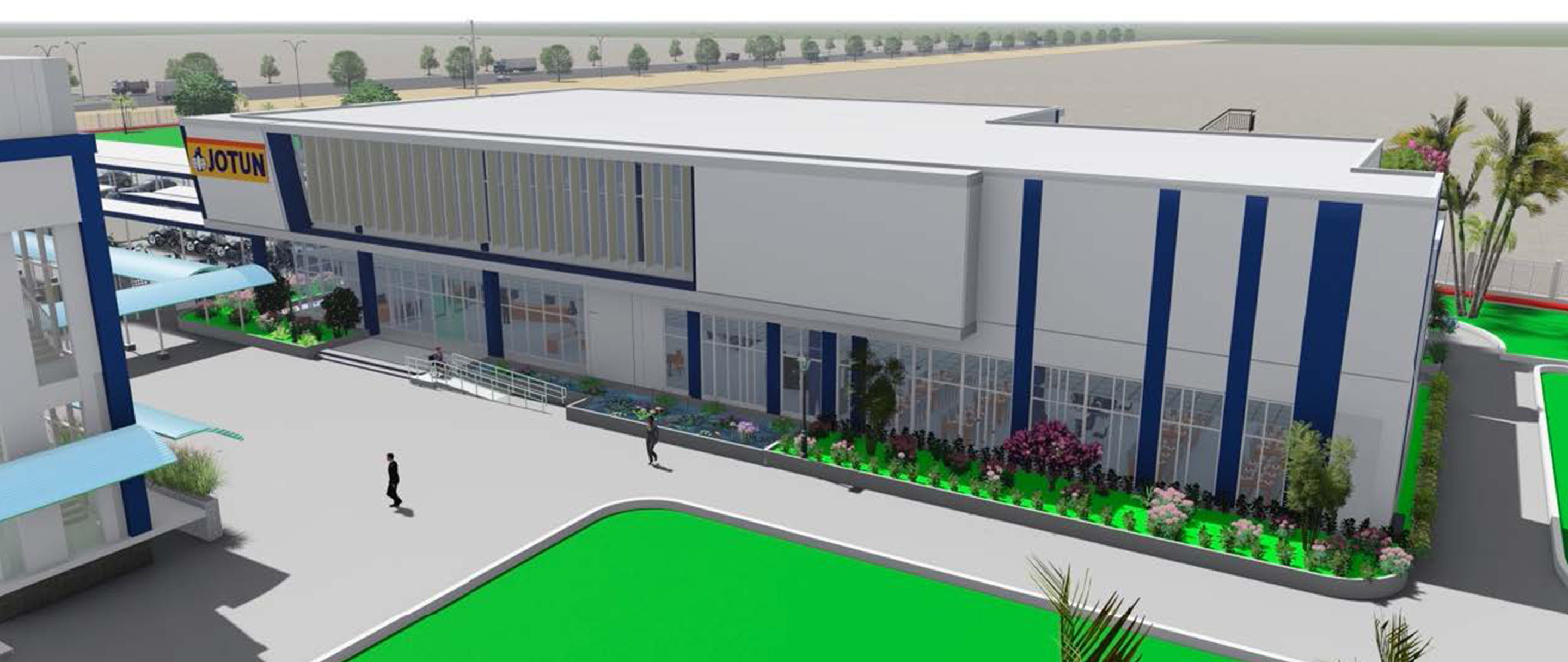

INTRODUCTION
Located Lot F3, Hiep Phuoc 2 Industrial Park, Nha Be District, HCM City, Vietnam, the project site is considered ideal for constructing a industrial manufacturing and create an eco-friendly and comfortable living environment, in accordance with standards of LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) Green Building Rating System.
There have been many conscious efforts toward "Go Green" for this project and sets the target of being a part of sustainability through LEED certification.
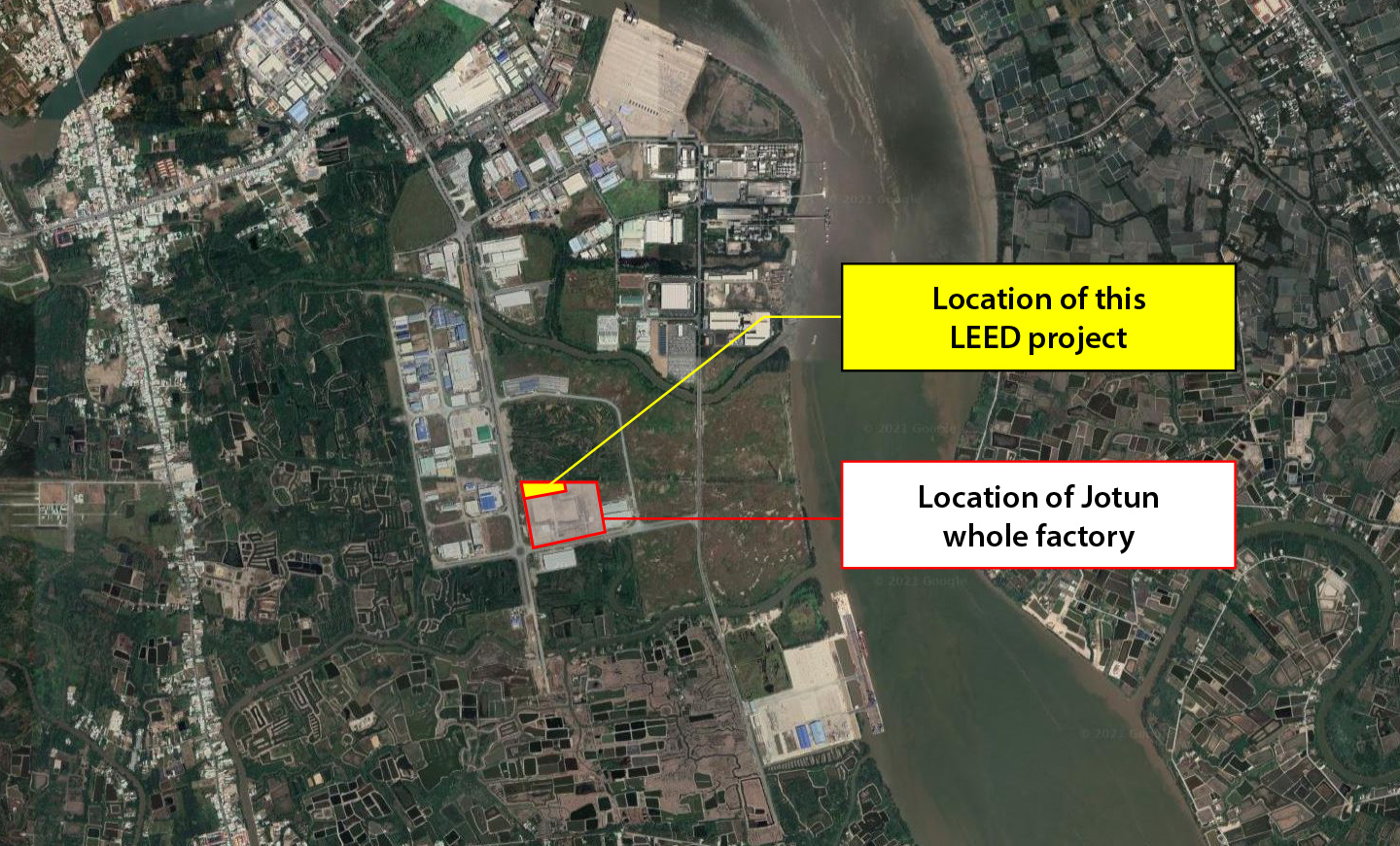
Being recognized by U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC) that the project has met all requirements of international environmental design standards, the project will have not only positive impacts on the environment but also result in significant reduction of operation costs. The effectiveness in the tower's performance are contribute from different factors such as lightning, vegetation, energy system, and glazing system, etc. Air quality, health and comfort, and relaxation are also focused to keep all staff and residents in their own comfort zone.

Key Highlights
- 47.04% of the total site area is green area and 47% open space, including green area and pedestrian area.
- Water-efficient fixtures and using alternative water sources for flushing toilet to reduce the potable water use by 87.25%.
- Effective landscaping with irrigation systems to reduce water demand by 56%.
- High efficiency (high COP) HVAC systems combine with solar panel system reduce energy cost by 73.6%.
- 100% LED light with high lighting efficiency.
In this case study, other highlighted features that make the project become a LEED-Gold certification building are also introducted in details.
SUSTAINABLE FEATURES
Building Envelope
Both the building's roof and floors are made of reinforced concrete. The 200-mm-thick roof has a total thermal transmittance U-value of 2.64 W/m2K while the external walls including concrete block, have a U-value of 1.9 W/m2K. The project uses Low-E glass for its external glazing system whose U-value are 2.5 W/m2K. This system works effectively to limit solar radiation, reduce energy loss, and provide daylighting for 89% of regularly occupied spaces. In other words, the glazing system limits the amount of heat and UV rays transmitted through glass, but still allows light to easily pass through the window. This contributes to the reduction of interior artificial lighting and cooling demand, resulting in energy cost reduction.

Daylighting
The project provides effective daylighting for above 75% of regularly occupied spaces. Shading manual blinds are installed on the facades to reduce glare for regularly occupied spaces.
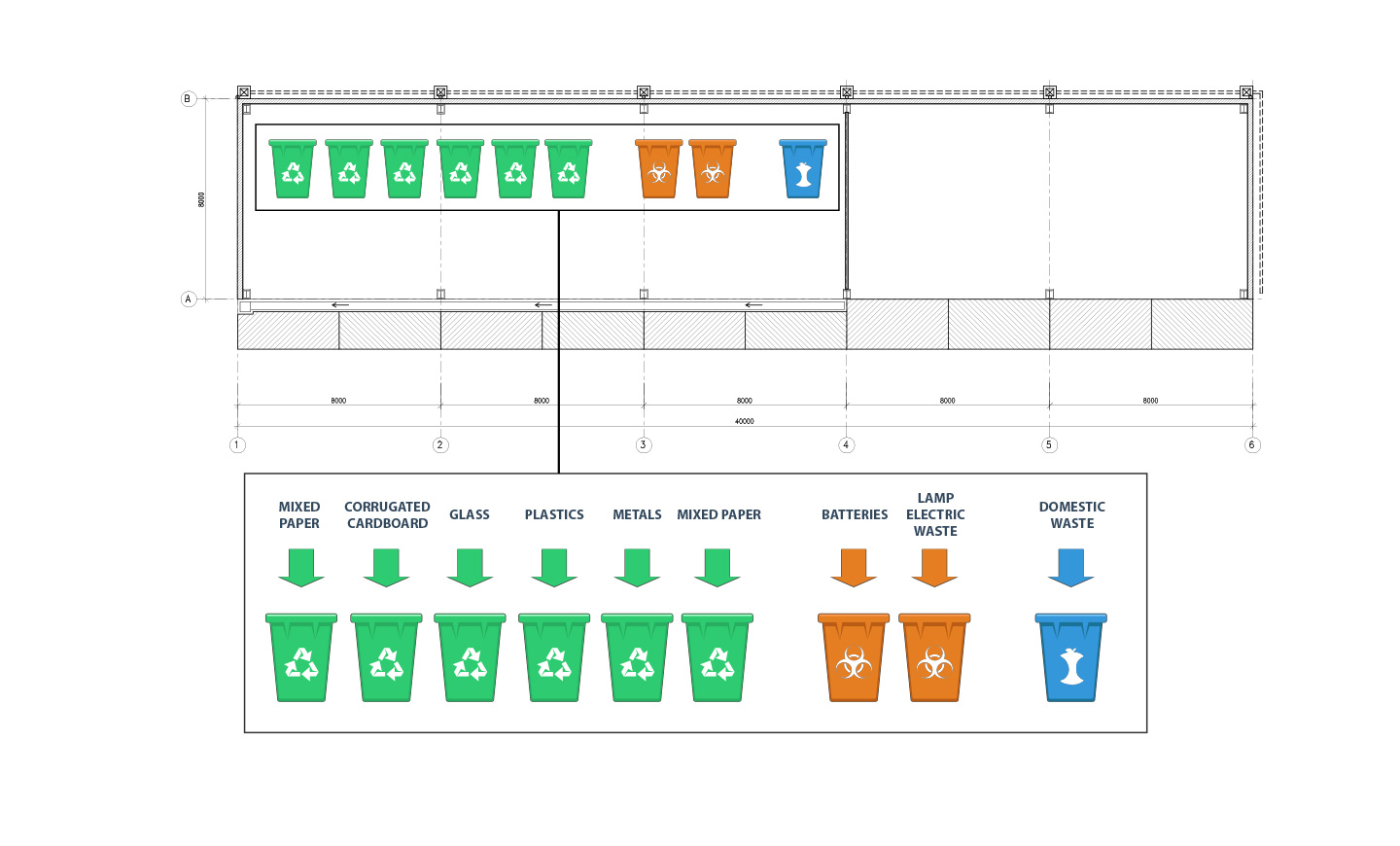
Waste Management
To reduce the amount of waste generated within the building and encourage everyone to sort waste, the project has designated a central waste storage at the basement. To ensure the waste storage capacity would be completely sufficient for the amount of waste generated, the project reserves a central waste storage which includes separate spaces for different types of waste such as recyclable waste, non-recycable waste, and hazardous waste. Labeled recyclable waste bins will be provided for plastics, paper, cardboard, glass, and metals. Other labeled bins are used for non-recyclable waste and hazardous waste (batteries and e-waste).
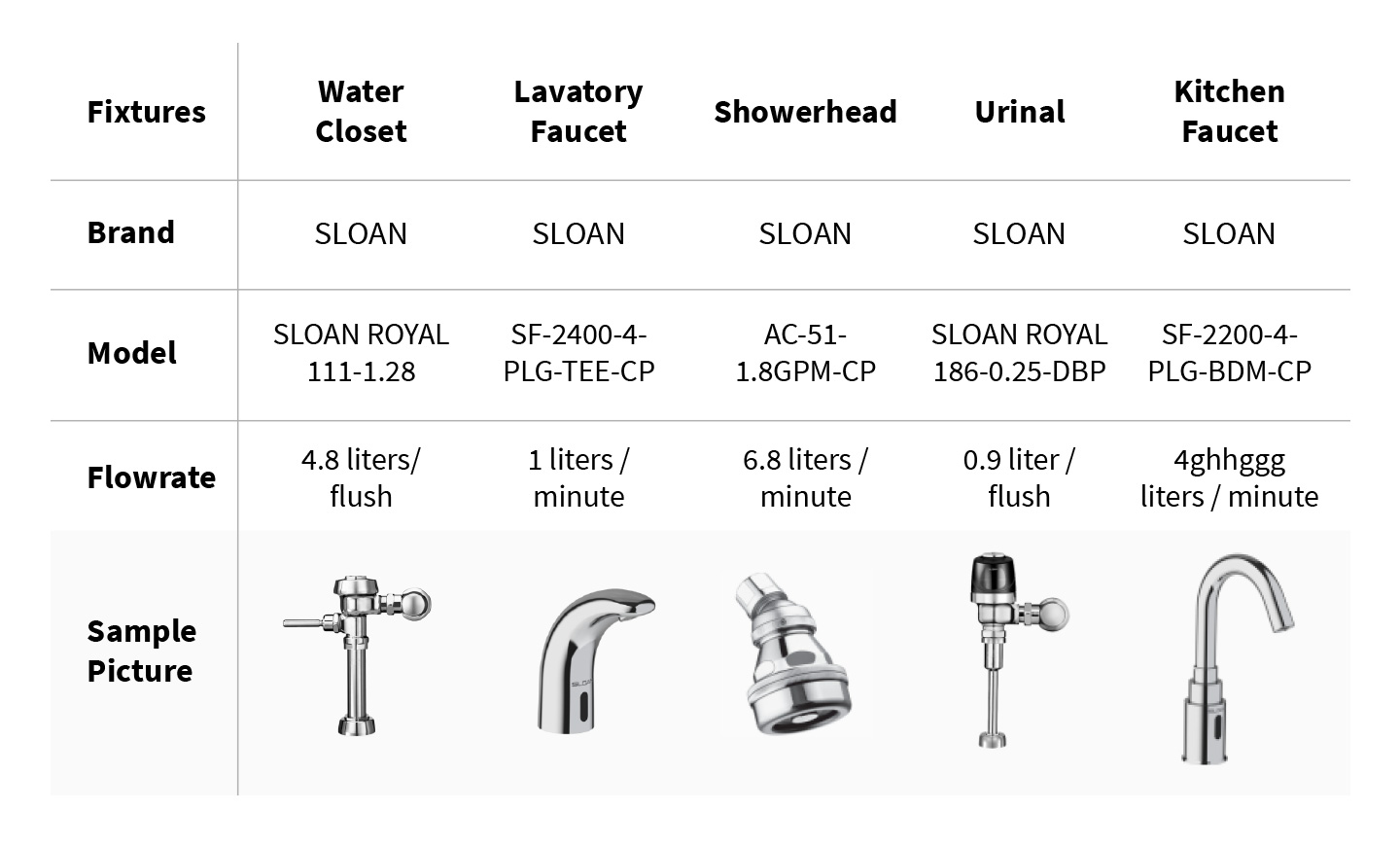
Indoor Water Use
The project aims to reduce indoor water consumption through using water-efficient fixtures such as low flowrate water closets, urinals, and lavatory faucets. The result achieved for indoor water use reduction is 36.58% compared to LEED baseline for indoor water use.
To reduce water at this project, the owner decided using Alternative Water (the treated wastewater) for flushing total percent indoor reduction from baseline : 87.25%.

Outdoor Water Use
For outdoor water use, selecting low irrigation demand plant species (trees, shrubs, and groundcover) and irrigation system (Drip & Fixed spray) helps the project save 56% potable water use for irrigation.
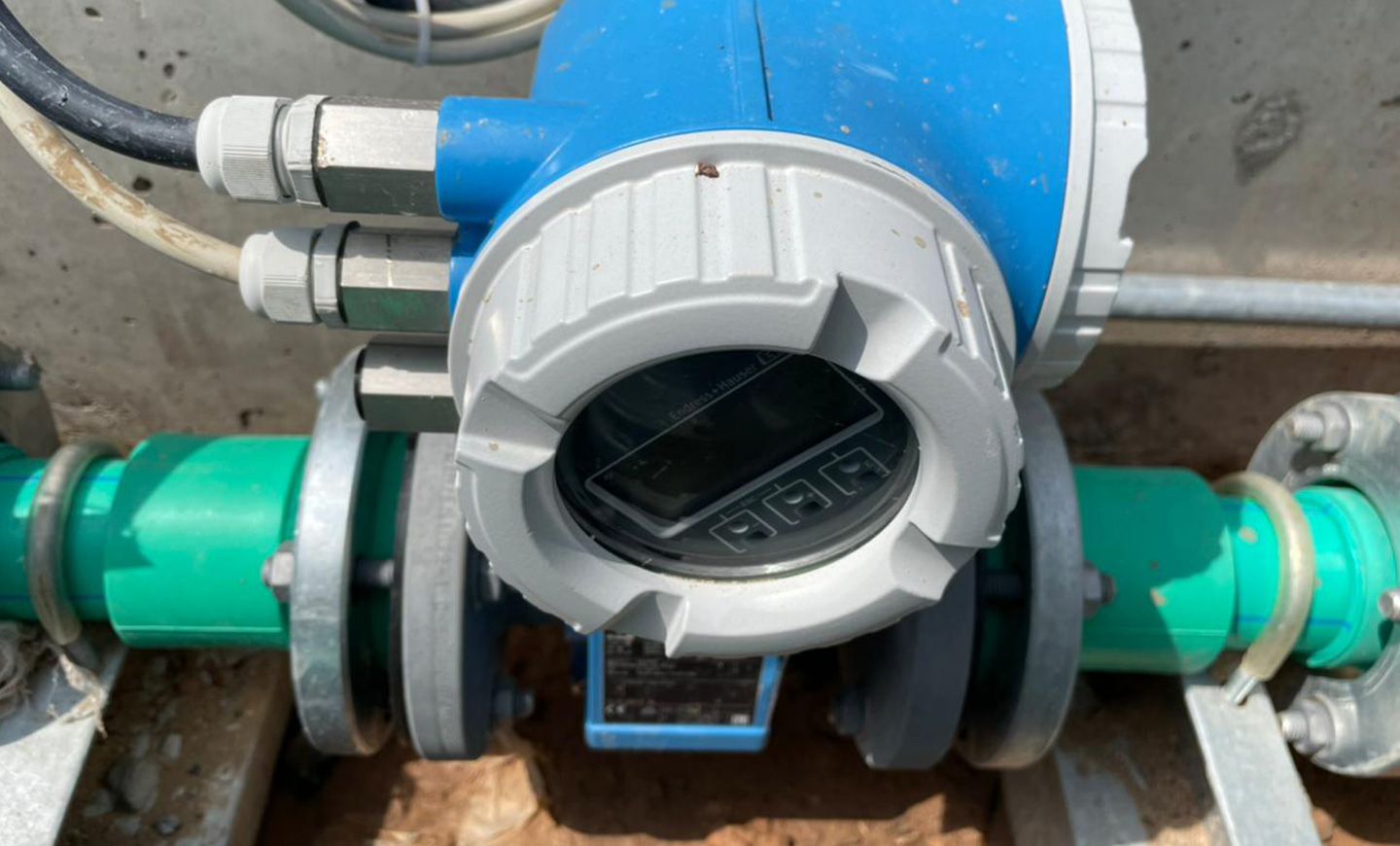

Water Metering
The project aims to manage water use and track water consumption by installing permanent water meters for all water subsystems. A system of 2 water meter and 6 water sub-meters have been installed to measure these water consumptions:
- Total potable water use for the building
- Total Reclaimed water (treated wastewater) use for indoor plumbing fixtures and fittings
- Total potable water use for process water
- Total potable water use for irrigation
Sub-meters will be manually read and periodically checked for monitoring purposes concerning water consumptions and potential damages.

Lighting
Lighting system of the building uses only LED lights for energy efficiency and savings. Motion sensors are installed in toilets, stairs, corridors, storages and Occupancy sensors are installed in meeting rooms, offices to automatically turn off lighting fixtures when nobody is in the room. Photo sensor are installed in daylighted areas. Time switch are installed exterior lighting to automatically turn off lighting fixtures in accordance with operational time.
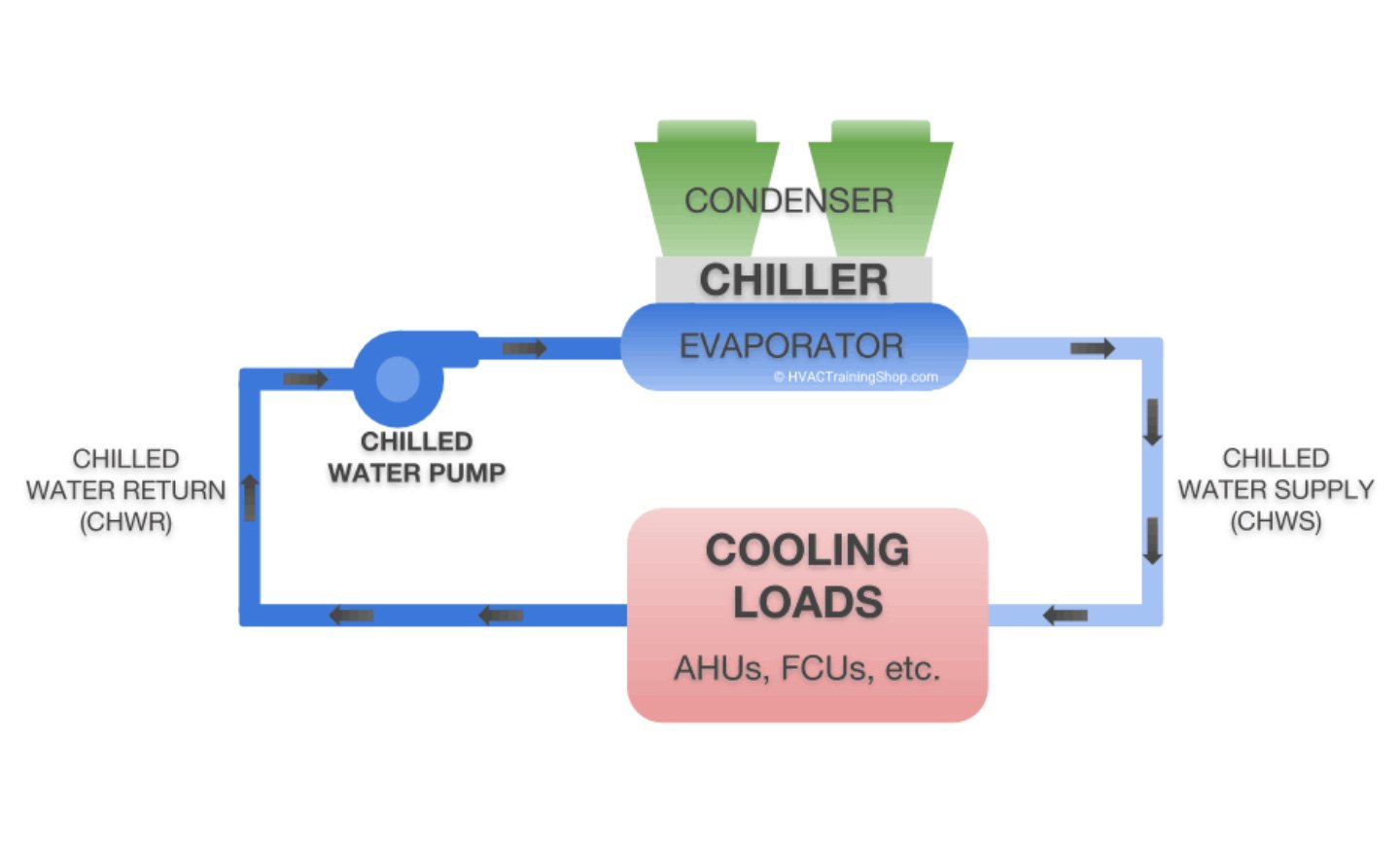
Air-conditioning & Ventilation
To optimize energy performance of the building as well as reduce environmental and economic harms associated with excessive energy use, the project uses air-cool chiller system.
Indoor air quality performance of this project ensured to contribute to the comfort and well-being of occupants (increase 30% air flow rate). Toilets and waste storages are ventilated by exhaust fans.
![]()
